🔵 Myrcene
🔵 Pinene
🔵 Limonene
🔵 Caryophylene
🔵 Linalool
🔵 Terpinalene
🔵 Camphene
The Patriots Relief Difference
Not all CBD is created equal
These days CBD is available almost anywhere, but the quality of the product may not be what you’re expecting. At Patriots Relief, our products are made with the purest, and most potent CBD available. Our proprietary extraction process uses the entire plant for a true full-spectrum oil, containing all the cannabinoids and compounds naturally found in medical cannabis. Our state-of-the-art extraction process ensures lipids, fats and other undesirable compounds are removed, resulting in an oil that is cleaner, higher potency, better looking, better tasting and more effective.


The complete plant profile
The complex biochemical interaction of the matrix of phytocannabinoids working synergistically in the body is referred to as the “entourage effect.” Cannabidiol is but one of more than 100 known phytocannabinoids that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS).
Patriots Relief’s TRUE Full Spectrum Phytocannabinoid-Rich (PCR) hemp oil contains a variety of synergistic compounds, including hundreds of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids which interact with one another to unlock the full power and potential of the plant. Only a TRUE Full Spectrum Hemp Oil Extract contains a complete array of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids.
Propriety Extraction
Our proprietary distillation process produces the highest quality oil in the world by removing impurities, including chlorophyll, lipids, waxes, and other destabilizing and undesirable compounds, resulting in an oil that is cleaner, higher potency, more effective, better looking and better tasting.
The Patriots Relief Advantage
Superior Plant Genetics
Our network of organic hemp farms are some of the largest in the country and our unique strains of cannabinoid-rich hemp are specially bred from the most medicinally high cannabidiol strains of medical cannabis. Stabilizing and cross-breeding results in superior plant genetics that allow our farmers to consistently grow pants that have the highest concentrations of CBD with the lowest levels of THC.
Our network of organic hemp farms are some of the largest in the country and our unique strains of cannabinoid-rich hemp are specially bred from the most medicinally high cannabidiol strains of medical cannabis. Stabilizing and cross-breeding results in superior plant genetics that allow our farmers to consistently grow pants that have the highest concentrations of CBD with the lowest levels of THC.


Proprietary Extraction
Our proprietary extraction process produces the highest quality oil in the world by removing all impurities, including chlorophyll, lipids, waxes, and other destabilizing and undesirable compounds.
Our extraction and purification processes take place at state-of-the-art extraction facilities where unique extraction technology allows for the highest levels of phytocannabinoids while eliminating unwanted amounts of THC and chlorophyll and leaving intact the full spectrum profile of non-psychoactive phytocannabinoids and synergistic compounds such as Cannabidiol (CBD), Cannabigerol (CBG), Cannabinol (CBN), and Cannabichromene (CBC). Additional steps of refinement are required to create our distillate oil wich is some of the purest oils available.
Key Cannabinoids Terpenes
"When terpenes work with cannabinoids like CBD, they form a sinergy that creates stronger and better effects than both would achieve on their own."
KEY CANNABINOIDS
Human Endocannabinoid System
While the body is making its own endogenous cannabinoids, many scientists suggest that most people are now “cannabinoid deficient”. Without enough cannabinoids in our diet, the HEcS will operate at less than its highest efficiency, resulting in an overall decline in overall health.
CB1 & CB2 Receptors
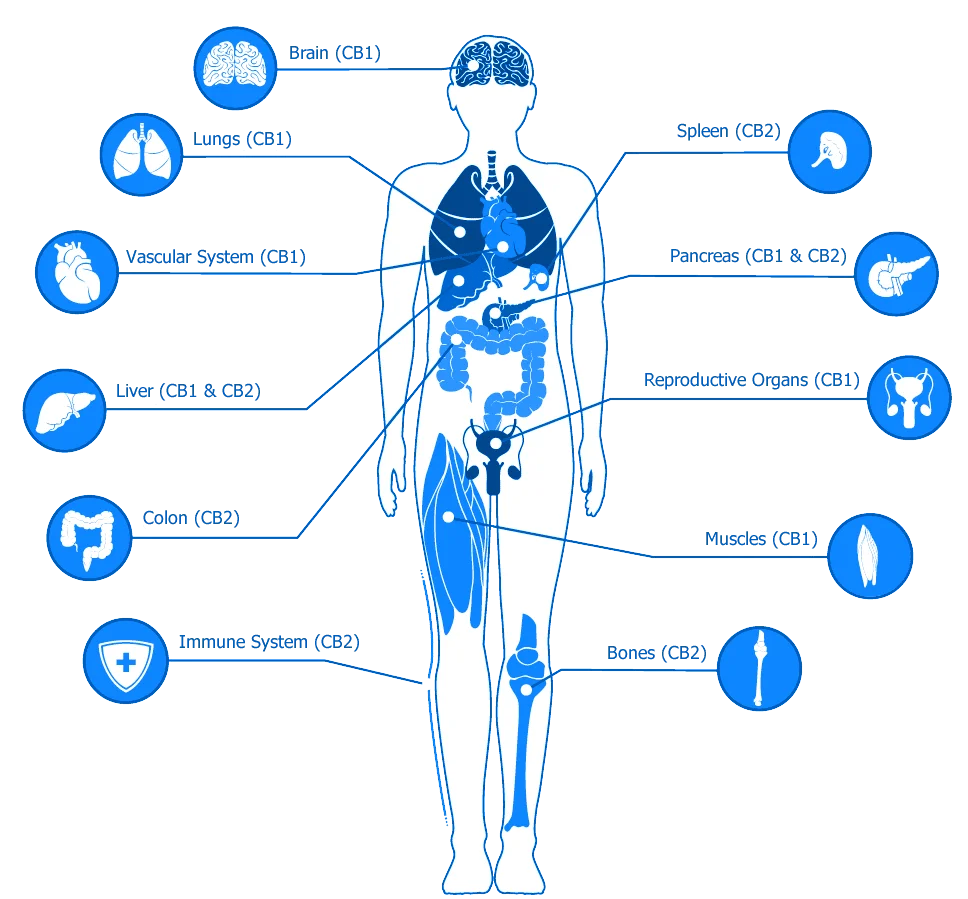
Scientists have only just begun to understand the importance of the Human Endocannabinoid System (HEcS). The discovery of the HEcS is arguably the most important discovery in human physiology in the late Twentieth Century. Research has revealed that the HEcS is responsible for maintaining and controlling the body’s homeostasis, or balanced regulation of every system in the body. It does that through two known receptors called CB1 & CB2.
While the body produces its own endogenous cannabinoids, many scientists suggest that most people are now suffering from “Cannabinoid Deficiency”. Without sufficient cannabinoids in our diet, the HEcS operates at less than peak efficiency, resulting in a general decline in overall health.
The primary cannabinoid receptors are identified as Cannabinoid Type 1 receptors (CB1-R) and Cannabinoid Type 2 receptors (CB2-R).
The receptors can be “unlocked” by three kinds of cannabinoids
Endocannabinoids
Endogenous-fatty-acid cannabinoids produced naturally in the body (e.g., anandamide and 2-AG)
Phytocannabinoids
Concentrated in the oily resin of the buds and leaves of plants such as Industrial Hemp plants (e.g., THC and CBD)
Synthetic Cannabinoids
Manufactured by artificial means such as in a laboratory
PhytoCannabinoids
Products from Patriots Relief use only Phytocannabinoids (Plant Based) NEVER Synthetic Cannabinoids.
The endocannabinoid system is found in every animal except insects and regulates a wide range of biological functions. The ECS is a biochemical control system for neuromodulatory lipids (molecules that contain fats, waxes, sterols, and fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A, D, E, and K, and others) and specialized receptors configured to accept certain cannabinoids. In general, a given receptor will only accept certain classes of compounds and will not be affected by other compounds, just like a certain key is needed to open a lock.
Specialized receptors are found throughout the human body, including, but not limited to, the hippocampus (memory, learning), the cerebral cortex (decision making, emotional behavior), the cerebellum (motor control, coordination), and the putamen (movement, learning), the hypothalamus (appetite, body temperature) and the amygdala (emotions). When a particular cannabinoid or combination of cannabinoids binds to a specialized receptor, an event or series of events is triggered in the cell, resulting in a change in the cell’s activity, its gene regulation and / or the signals it sends to neighbors sends cells. This process is known as “signal transmission”.
Science, which was first demonstrated in the brain, now shows that CB1-R is also found in many other organs, connective tissues and glands. CB1-R are not found in the medulla oblongata (the part of the brain stem responsible for respiratory and cardiovascular functions). CB1-R plays an important role in the coordination of movements, spatial orientation, sensory perceptions (taste, touch, smell, hearing), cognitive performance and motivation.
The most important function of the CB1-R is to reduce excessive or insufficient signals from the neurotransmitters (messenger substances) in the brain. By activating the CB1-R, the hyperactivity or hypoactivity of the messenger substances (e.g. serotonin, dopamine) is brought back into balance.
CB2-R are primarily associated with the immune system and are located outside the brain in places such as the intestines, spleen, liver, heart, kidneys, bones, blood vessels, lymph cells, endocrine glands, and reproductive organs. Until recently, it was believed that CB-2R did not play a role in nerve cells or bundles. However, studies now show that it also plays an important role in the brain’s signal processing.
A third receptor that has received little attention is the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1). The function of TRPV1 is to sense and regulate body temperature. In addition, TRPVXNUMX is responsible for the sensations of extreme external heat and pain and is subject to desensitization. If the path is continuously stimulated, it will eventually slow down or even stop.





